However the anode of a galvanic cell is negatively charged since the spontaneous oxidation at the anode is the source. 1 Get a strip of each of the metals youre investigating.

Difference Between Galvanic Cell Chemistry Projects Chemistry Basics
2 Which energy conversion occurs in a voltaic cell.
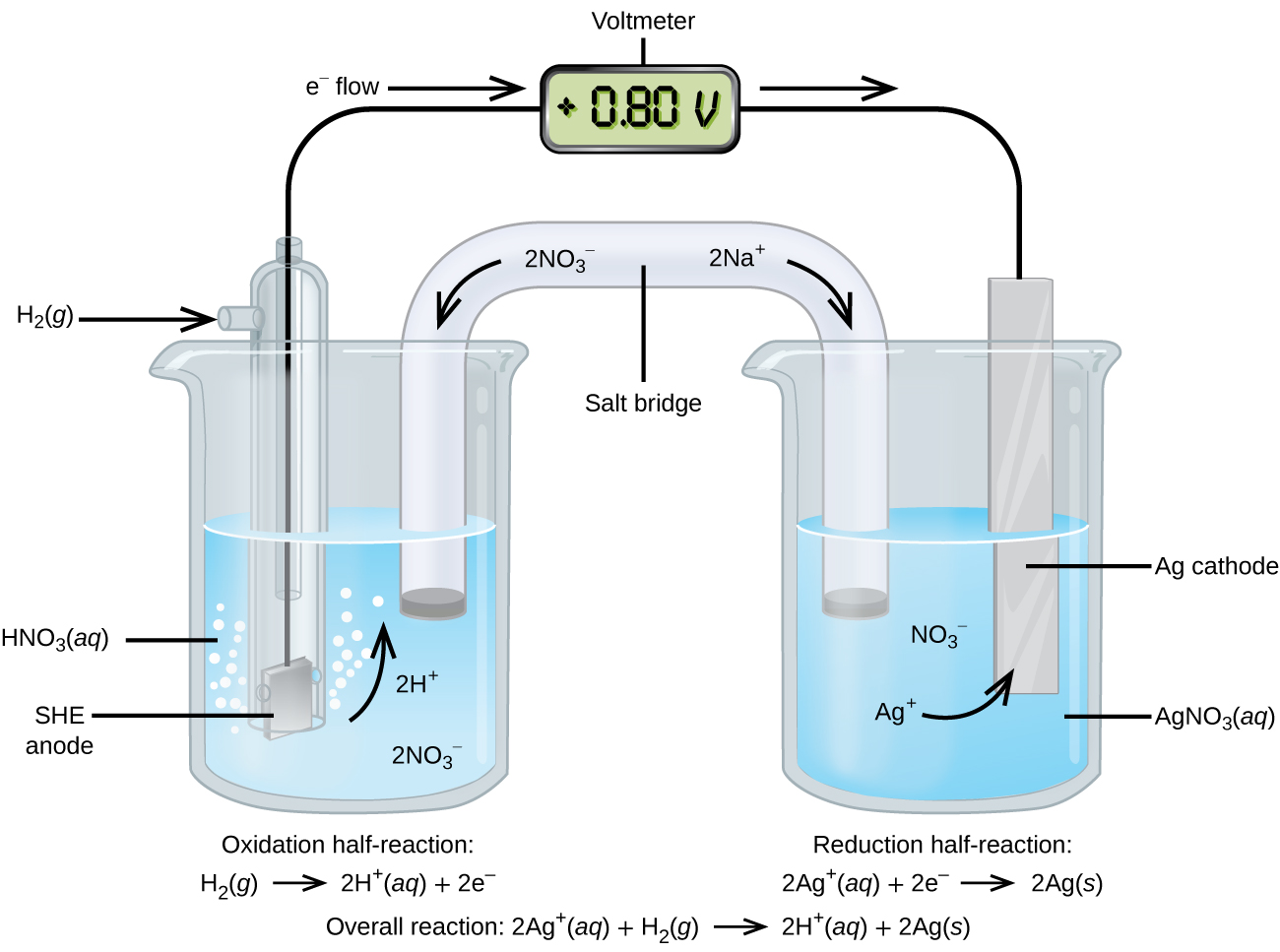
. It is defined as the cell in which the chemical reaction occurs with the production of electric potential difference between the two electrodes. In an electrolytic cell oxidation occurs at the positive electrode also called the anode. In any electrochemical cell reduction occurs at the cathode.
12 What is the difference between a voltaic cell and an electrolytic cell quizlet. 13 Why do anions flow toward the anode. Oxidation occurs at the electrode termed the anode and reduction occurs at the electrode called the cathode.
One is cathode and the other one is anode. For this purpose 2 rods or electrodes are kept in the chemical solution. The direction of electron flow in electrolytic cells however may be reversed from the direction of spontaneous electron flow in galvanic cells but the definition of both cathode and anode remain the same.
A method to construct an electrochemical cell involving two metals. 11 What happens at the cathode in an electrolytic cell. Oxidation occurs at the electrode termed the anode and reduction occurs at the electrode called the cathode.
In an electrochemicall cell reduction takes place in thecathode. At the cathode At the anode In the salt bridge At both electrodes. Why does the cathode carry a negative charge when electrolysis occurs rather than the positive charge it.
In an acidic aqueous solution Hydrogen will be generated however some metals require an overvoltage. In an electrochemical cell reduction takes place at anode BECAUSE oxidation always takes place at the cathode. H ions act as the oxidising agent gaining electrons to become hydrogen molecules.
15 Where does reduction occur in an electrolytic cell. By Da_Irene256 08 Apr 2022 Post a Comment Keywords are used to define the syntax of the coding. 14 Why electrolytic.
7 What happens in a voltaic cell. 1 at the cathode in both an electrolytic cell and a voltaic cell 2 at the cathode in an electrolytic cell and at the anode in a voltaic cell 3 at the anode in both an electrolytic cell and a voltaic cell 4 at the anode in an electrolytic cell and at the cathode in a voltaic cell. O at the cathode O at the anode O at.
3 What conversion process takes place in an electrolytic cell. 7 How does electrolysis produce hydrogen. 12 What are electrodes made of.
In an electrolytic cell oxidation occurs at the anode positive electrode while reduction occurs at the cathode negative electrode. 6 Which energy conversion shown below takes place in a voltaic cell. The electrode at which oxidation takes place in a electrochemical cell is called the anode.
The anode of an electrolytic cell is positive cathode is negative since the anode attracts anions from the solution. 11 Is voltaic cell an electrolytic cell. Electrolytic cells like galvanic cells are composed of two half-cells--one is a reduction half-cell the other is an oxidation half-cell.
The anode of an electrolytic cell is positive cathode is negative since the anode attracts anions from the. Anode is the electrode at which oxidation takes place and the sign of the electrode is positive and Cathode is the electrode at which reduction takes place. Chemistry questions and answers.
Transcribed image text. E The overall equation is as follows. Where does reduction occur in an electrochemical cell.
When the circuit is closed electrons flow from the anode to the cathode. 16 How do you make voltaic cell. In an electrochemical cell where does the reduction occur.
The electrode at which reduction occurs is called the cathode. In other words H ions undergo reduction. These are your electrodes.
Answer 1 of 3. 14 What happens in a voltaic cell quizlet. In this electrolytic cell the oxidation occurs at anode which is a positive electrode and reduction occurs at cathode which is a negative electrode.
Ox Keywords No wallpaper. In both galvanic and electrolytic cells oxidation takes place at the anode and electrons flow from the anode to the cathode. 13 Which energy conversion must occur in an operating electrolytic cell.
The identity of the cathode and anode can be remembered by recognizing that positive ions or cations flow toward the cathode while negative ions or anions flow toward the anode. 5 Where does reduction occur in a voltaic cell. 10 What drives an electrolytic cell.
And reduction takes place at cathode. 8 How does an electrochemical cell produce current in a circuit. And reduction takes place at cathode.
Depends on the contents of the cell. The half-cell where oxidation happens the anode should always be drawn on the left and the half-cell where reduction happens the cathode is drawn on the right. Electrolytic cells are the cells which convert electrical energy into chemical energy.
The oxidation half-reaction occurs at one electrode the anode and the reduction half-reaction occurs at the other the cathode. Where does oxidation occur in an electrochemical cell. In any electrochemical cell reduction occurs at the cathode.
The oxidation number of an element decreases an element gains electrons compound loses Oxygen or the compound gains Hydrogen. 9 Is electrolytic cell same as electrochemical cell. If it is a metal salt and the cathode potential is high enough then the metal will precipitate plate out of the solution unto the cathode.
Announced they no longer use the meta keywords tag anymore either. See answer 1 Best Answer. 4 What is a key difference between an electrolytic cell and a voltaic cell.
At the negative electrode cathode the reverse occurs.
Electrochemical Cells In An Electrochemical Cell We Physically Separate The Oxidation And Reduction Chemistry In Different Compartments The Electrons From The Oxidation Are Then Run Through An External Circuit Before Being Used In The Reduction Reaction
0 Comments